Fine-Tuning Memory Allocation by Antivirus Software

Fine-Tuning Memory Allocation by Antivirus Software
If you’ve kept a close eye on the Task Manager, then you may have noticed the Antimalware Service Executable doing its job. It is a crucial process of Windows Security (previously “Microsoft Defender”) and helps keep your system safe from malware. It is pretty common to disable the Antimalware Service Executable because it consumes a large chunk of the system resources.
On older PCs with limited system resources, the Antimalware Service Executable can severely impact the performance of your system. Read on as we discuss the importance of this service and how you can disable it.
Disclaimer: This post includes affiliate links
If you click on a link and make a purchase, I may receive a commission at no extra cost to you.
What Is the Antimalware Service Executable?
You’re probably familiar with Windows Security (previously Microsoft Defender). Windows Security is a reliable antivirus that comes pre-installed on Windows 10 and 11. The Antimalware Service Executable (you may find it listed asMsMpEng.exe in theTask Manager) is a core part of Windows Security.
The service helps ensure your PC stays protected against any virus, worms, and other malware by continually scanning files and programs on your PC in the background. If the Antimalware Service Executable finds a malicious file or program, it will immediately delete or quarantine the affected files.
Should You Disable the Antimalware Service Executable?
Considering how integral the Antimalware Service Executable is to protect your PC, you must be wondering why you should even consider disabling it.
If you do not have a third-party antivirus installed on your system, then Windows Security is your sole protection against potentially harmful malware. If your PC is left without any third-party antivirus programs installed, the Antimalware Service Executable automatically enables itself and begins safeguarding your PC as part of Windows Security.
Ideally, you should not turn off the Antimalware Service Executable process. But if you have a reliable third-party antivirus installed, and the Antimalware Service Executable is still consuming a large chunk of your RAM or CPU, then it might make sense to disable it.
How to Disable the Antimalware Service Executable
There are a few different ways you can disable the Antimalware Service Executable depending on the circumstances of your system’s performance.
Method 1: Disable Real-time Protection
Suppose you find the Antimalware Service Executable process consuming a lot of system resources in certain instances; in that case, you can temporarily disablereal-time malware protection through Windows Security:
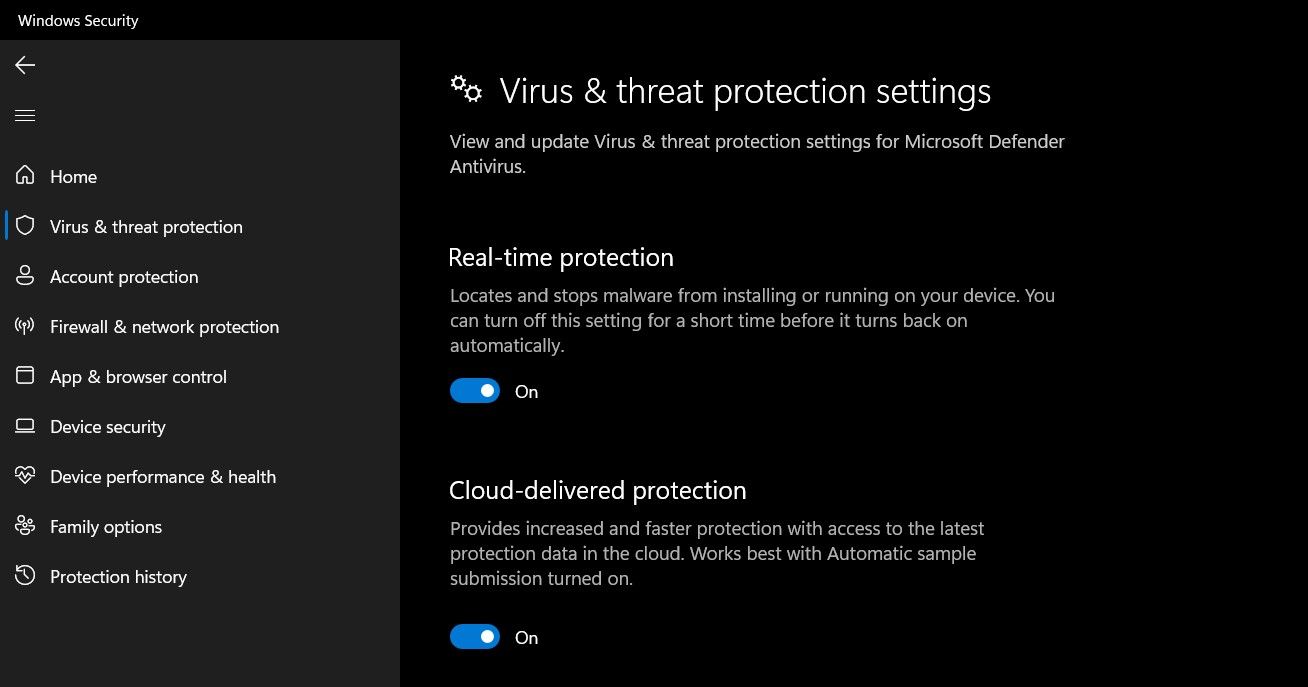
- Head to theStart menu, search forWindows Security and select the Best match.
- Navigate toVirus & threat protection from the sidebar.
- Look forVirus & threat protection settings , and then click onManage settings option underneath.

- Disable theReal-time protection toggle button by bringing it to theOff position.
Real-time protection will be turned back on automatically by Windows Security.
Method 2: Turn Off Antimalware Service Executable Through Windows Security in the Registry Editor
For users looking for a more permanent solution to disabling the Antimalware Service Executable, you will have todisable Windows Security from the Registry Editor.
If you do not have a third-party antivirus installed, disabling Windows Security will leave your system at risk of malicious malware that can damage it.
To disable Antimalware Service Executable from the Registry Editor:
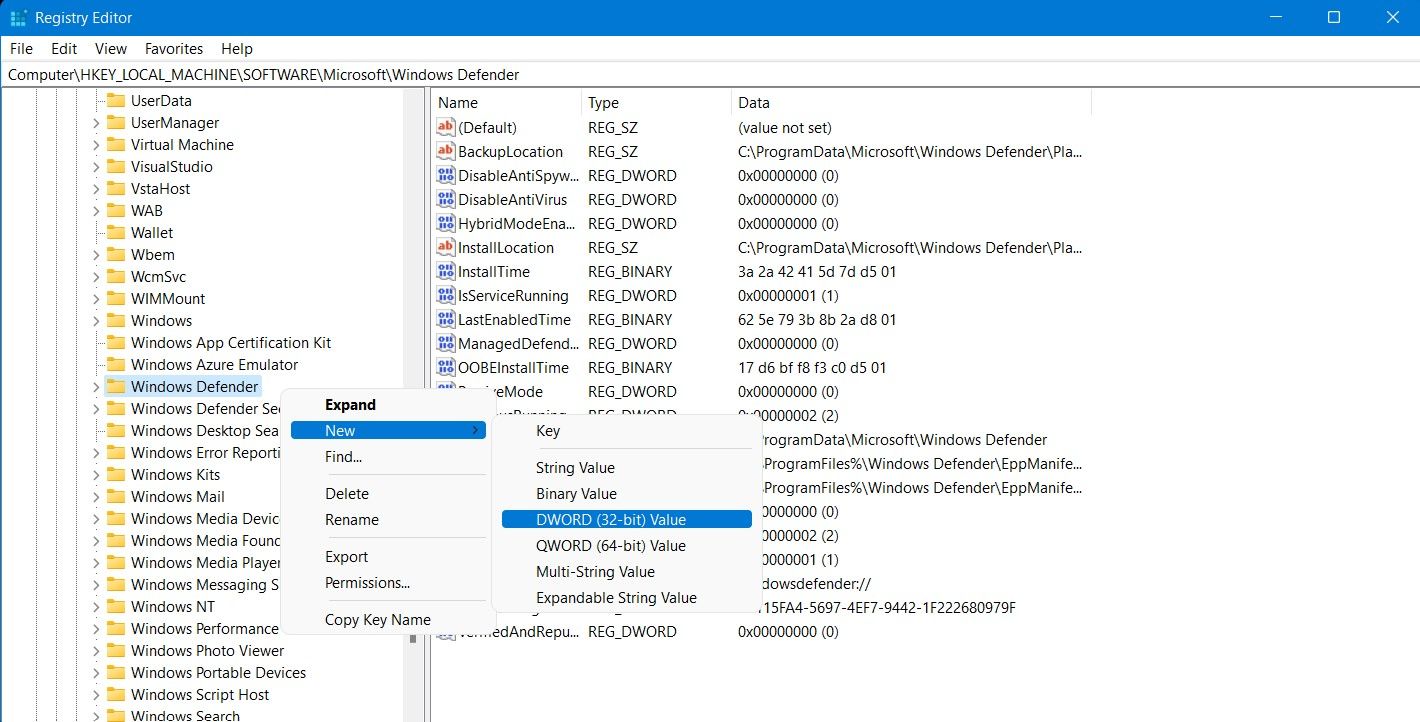
- Search forRegistry Editor from theStart menu, and launch it.
- Navigate to HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE > SOFTWARE > Microsoft > Windows Defender from the sidebar.
- Right-click on theWindows Defender folder and selectNew > DWORD (32-bit) Value .

- EnterDisableAntiSpyware in theValue name field and1 in theValue data field.
- PressOK to save your changes and restart your system for the changes to take effect.
Should You Rely on Windows Security for Windows 10 and 11?
Many users opt for a dedicated third-party antivirus on Windows 10 or 11, but Windows Security has made significant improvements in the past few years. Not only is Windows Security a complete antivirus package, but it’s also free and comes pre-installed on Windows.
Also read:
- [New] FB Video Mastery Effortless MP4 Extraction
- [New] In Pixels We Trust A Guide to Photomontages
- [Updated] YouTube Cash Flow 8 Simple Money-Making Tips
- 9 Best Free Android Monitoring Apps to Monitor Phone Remotely For your Motorola Defy 2 | Dr.fone
- Accessing & Understanding Windows Component Services Interface
- Accessing Windows 11 Safe Mode: 6 Routes Covered
- Addressing GPU Thermal Spikes During Play
- App Aesthetics Overshadowing Computational Efficiency Issues
- Avoid Unwanted Updates in Windows 11 with Proactive Measures
- Best 10 Mock Location Apps Worth Trying On Vivo S17 Pro | Dr.fone
- Boost Your Computer's Space on Windows Using These Free Tools
- Does Galaxy F54 5G has native MOV support?
- Enhance Real-Time Play with Lower Latency
- Full Powered Computing on the Go – Folding Mini Keyboard Houses AMD Ryzen CPU, Touchscreen Controls, and Self-Contained Battery; Just Add a Display!
- In 2024, Sim Unlock Honor X8b Phones without Code 2 Ways to Remove Android Sim Lock
- Update Drivers: Make Sure Your Graphics Card Drivers Are up to Date for Optimal Performance.
- Title: Fine-Tuning Memory Allocation by Antivirus Software
- Author: Richard
- Created at : 2024-09-26 20:20:57
- Updated at : 2024-10-03 16:00:11
- Link: https://win11-tips.techidaily.com/fine-tuning-memory-allocation-by-antivirus-software/
- License: This work is licensed under CC BY-NC-SA 4.0.