
Navigating the Complexities of Docker with WSL 2

Navigating the Complexities of Docker with WSL 2
The Windows Subsystem for Linux 2 is a phenomenal tool on Windows 10 and 11, and integrates with Docker seamlessly. As developers, it’s essential to understand what these software offers and how you can make the most out of your Docker-WSL 2 setup.
What Is Docker?
Docker is an open-source platform that allows developers to efficiently build, deploy and run their applications within a container. All dependencies are bundled up so your project can easily be deployed in any environment.
Docker is very popular among many containerization platforms because it is reliable, functional, and highly scalable. It runs on the Docker engine, an essential DevOps tool that provides a clean and lightweight environment for testing and deployment. Docker is similar to a virtual machine but virtualizes the operating system rather than the underlying hardware.
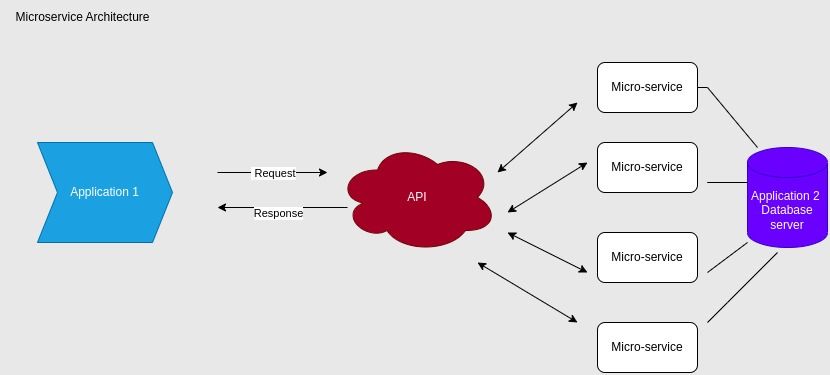
For software developers, Docker streamlines workflow by creating individual containers for different microservices that include the necessary dependencies, libraries, and configurations. Each microservice container is isolated and individually scalable.
How to Use Docker on WSL 2
Docker is compatible with all major operating systems, such as Windows, macOS, and Linux. If you’re on Windows 10 or 11, you can use Docker via Docker Desktop and integrate it with the Windows Subsystem for Linux 2 for improved performance. You can download Docker Desktop for Windows from the official Docker website .
The Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL) is a valuable feature that allows Windows users to run Linux distributions like Ubuntu and Kali without setting up a virtual machine or dual-boot.
This also means that Windows users can directly use Linux command-line tools , applications, and utilities without extra installation steps. The most recent version of WSL, WSL 2, provides greater stability and a dedicated Linux kernel.
Since Docker containers are robust, you can even configure them to host your server; nginx docker containers are commonly used as web servers. Additionally, you can use Docker in several other ways:
- Run Linux distros easily
- Set up a web server for learning or testing purposes
- Portable deploy applications
- Bundle the application into a single image file
- Simplified CI/CD pipeline
You must become familiar with the best practices for utilizing Docker with Windows Subsystem for Linux 2, just like you would with any other platform or tool. As a developer, I can say from personal experience that you’ll become much more productive and efficient once you integrate the following tips into your workflow.
1. Integrate VS Code with WSL 2
Visual Studio Code is a popular IDE that’s loved due to its incredible features, community, and extensions. As a developer, the ability to use Visual Studio Code for app development on a Windows platform while also running those apps on a Linux kernel is an incredibly advantageous and almost unbelievable feature.
When you integrate VS Code into the Windows Subsystem for Linux, you can take advantage of its specialized Linux kernel to enhance cross-platform compatibility. You can further streamline your workflow by utilizing the integrated terminal within VS Code with WSL 2.
To set up VS Code with WSL 2 on Windows , you can configure theWSL extension from the VS Code Marketplace and get things going.
2. Utilize the WSL 2 File System
To properly run your Docker containers, it’s vital that you rely on the file system of your WSL 2 distro and not heavily depend on the native Windows file system. Throughout my experience of working with Docker containers on WSL 2, I’ve discovered it’s better to store your project files within WSL.
 ZoneAlarm Pro Antivirus + Firewall NextGen
ZoneAlarm Pro Antivirus + Firewall NextGen
3. Use Native Linux Scripts
Many containerized projects that you’ll work on will probably come with scripts for automation on Linux. Typically, these scripts are first developed for Linux, and Windows developers aren’t a priority.
With WSL 2, your entire team can use the same Linux automation scripts, and you don’t have to worry about maintaining Windows-compatible automation scripts for your team.
4. Configure BuildKit for Improved Security and Performance
BuildKit is an open-source toolkit that improves the traditional Docker build process in terms of performance and security; it’s directly integrated with Docker, so you don’t need to install it separately.
When you enable theBuildKit by default, you’re making sure that your containers are being built with the BuildKit toolkit, giving you better security, concurrency, flexibility, and caching.
To enable BuildKit by default, you should make the following changes to the ~/.profile config file:
export DOCKER_BUILDKIT=1.
 Power Tools add-on for Google Sheets, 12-month subscription
Power Tools add-on for Google Sheets, 12-month subscription
5. Set Up Resource Limits
When you integrate the WSL 2 backend with Docker Desktop, you give Docker access to all your CPU resources. Doing so helps improve performance for containers that are resource heavy.
However, in some cases, a container might allocate a lot of excess memory, causing critical OS processes to crash. You’re more likely to experience this when using database containers or a caching microservice.
Fortunately, you can configure Docker containers to limit the system memory and CPU usage. You should always be careful while configuring the system memory, even a minor mistake can have significant consequences. You can refer to the official Docker documentation for a more detailed guide on limiting the memory and CPU resources consumed by a Docker container.
6. Recover Cached Memory
If you’re running a Docker container in WSL 2, its memory should be freed once the container terminates. Unfortunately, the operating system kernel tends to maintain data in the cache; this means that the effective memory reclaimed by the WSL 2 won’t be sufficient.
You can recover all of the memory that is unnecessarily being utilized as a cache by running the following command via root in WSL 2:
echo 1 > /proc/sys/vm/drop_caches
Get Smarter With WSL 2
The WSL 2 is the best feature for Windows-based developers, completely changing how developers use Docker. Developers must understand the best practices for using Docker with WSL to improve performance, security, and workflow flexibility.
- Title: Navigating the Complexities of Docker with WSL 2
- Author: Richard
- Created at : 2024-08-16 02:11:22
- Updated at : 2024-08-17 02:11:22
- Link: https://win11-tips.techidaily.com/navigating-the-complexities-of-docker-with-wsl-2/
- License: This work is licensed under CC BY-NC-SA 4.0.

