Scaling Back Resource Usage by TiWorker.exe on Windows

Scaling Back Resource Usage by TiWorker.exe on Windows
Did you recently find that your Windows system is running slowly, and your CPU usage has skyrocketed? Chances are the culprit behind these issues is TiWorker.exe - a Windows system process that runs in the background and can take up high amounts of CPU resources if it encounters errors. In this article, we’ll explain what TiWorker.exe is and how to fix errors related to it.
Disclaimer: This post includes affiliate links
If you click on a link and make a purchase, I may receive a commission at no extra cost to you.
What Is TiWorker.exe?
TiWorker.exe is a legitimate system process that executes background tasks on Windows. It is associated with the Windows Update service and installs and manages system updates. This process runs automatically whenever the system is idle, or you can manually trigger it by clicking “check for updates” on Windows.
TiWorker.exe poses no security threat and is generally safe to run in the background. However, it can cause excessive CPU usage if it encounters errors during its execution, which can slow your computer down and lag. Therefore, you must identify the root cause of TiWorker.exe-related errors and fix them.
Below, we’ll look at some of the most common fixes for TiWorker.exe’s high CPU usage.
1. Run the Windows Update Troubleshooter
The Windows Update Troubleshooter can detect and fix most problems that cause TiWorker.exe to take up excessive CPU resources. To run the troubleshooter, do the following.
- Press Win + I on your keyboard to open the Settings app.
- In the Settings menu, select System from the left pane.
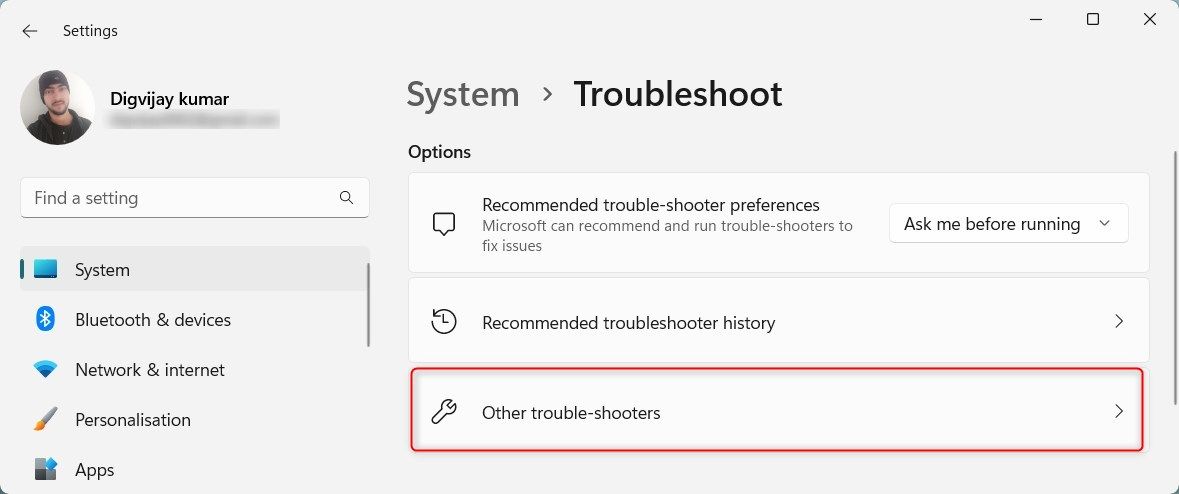
- Click Other troubeshooters on the next page.

- Locate Windows Update and click the Run button.
This should detect and fix any errors that are causing TiWorker.exe to take up too much CPU usage. Once the process completes, restart your computer and check if TiWorker.exe is still consuming high CPU resources.
2. Run the System Maintenance Troubleshooter
You can also run the System Maintenance Troubleshooter to fix TiWorker.exe-related errors. It detects and fixes disk fragmentation, registry problems, and other errors that cause TiWorker.exe to take up too much CPU.
To run the troubleshooter, follow these steps:
- Right-click on Start and select Run from the menu list.
- In the dialog box, type the following and hit Enter:
%systemroot%\system32\msdt.exe -id MaintenanceDiagnostic - The System Maintenance Troubleshooter will now open.
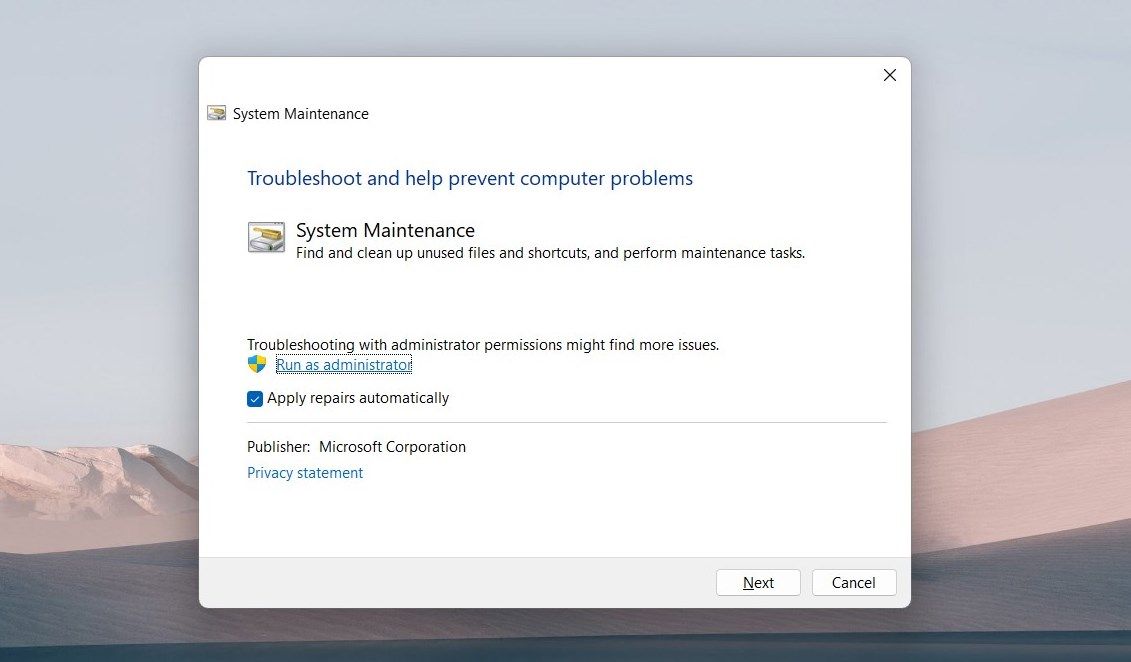
- On the Troubleshooter page, click Advanced.

- Check Apply repairs automatically and click Run as administrator.
- Click Next and follow the instructions to complete the process.
Once you finish running the troubleshooter, restart your computer and see if it solves the issue.
3. Clear the Software Distribution Folder
The Software Distribution folder stores temporary files associated with Windows updates. If this folder gets cluttered, TiWorker.exe may consume too many CPU resources. To fix this, you can delete the Software Distribution directory and let Windows create a new one. Here’s how to do this:
- Press the Win + R shortcut key to open the Run window.
- Type services.msc in the dialog box and click OK.
- Find Windows Update in the Services list and double-click it.
- In the Properties window, select Stop under the Service status section.
- Now press Win + E on your keyboard to open File Explorer.

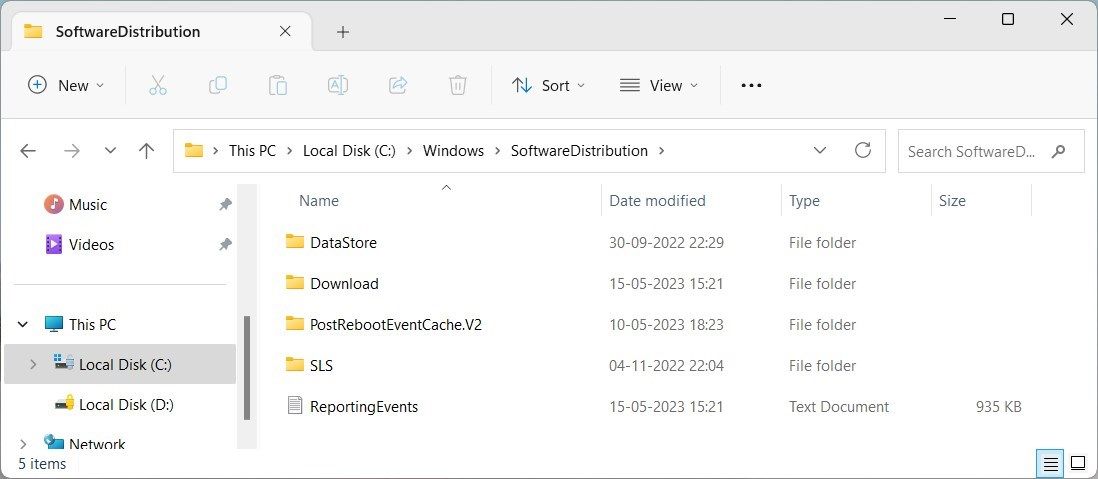
- Navigate to C:\Windows\SoftwareDistribution and delete all files and folders in this directory.
You can copy and paste C:\Windows\SoftwareDistribution in the File Explorer address bar and hit Enter to access the folder directly.
7. Now close File Explorer and go back to the Services window.
8. Scroll down to Windows Update, right-click on it and select Start to restart the service.
After you complete these steps, restart your computer and check if TiWorker.exe is still taking up too much CPU usage. If so, continue to the next solution.
4. Perform Several General Fixes
If none of the above solutions help, you can try performing some general fixes to fix the TiWorker.exe issue. These include running system file checker to detect and repair corrupted system files.
You can also try performing a clean boot , which disables all third-party applications and services and helps you identify the cause of TiWorker.exe’s high CPU usage.
Managing High CPU Usage on Windows
High CPU usage can cause your computer to become slow and laggy, disrupting your daily activities. Now that you’ve tried these tips, your Windows experience should be faster and smoother.
Also read:
- [New] 2024 Approved Balancing Act Tripod Use for Stable Vlogging
- [New] 2024 Approved Enhancing Video Reach Tactics Against Bot Visitors
- [Updated] Create Compelling Animation Subscribe Bars for Your YouTube Channel (Filmora) for 2024
- 2024 Approved Top Applications for Remote Team Connection
- A Step-by-Step Approach: Using the Netstat Command in Win11
- Comparative Analysis: Understanding the Variance Between Non-Microsoft and Microsoft Account in OS
- Download & Update Driver Pack for Intel Wi-Fi 6 AX200 on Your PC (Windows 11/10)
- Easy Steps: Dell Speakers Software Updates and Downloads
- Efficient Storage: Activating Windows 11’S Compression
- How to Bypass iPhone SE (2020) Passcode Easily Video Inside
- Mastering Service Setups for an Immaculate Windows 11 Launch Experience
- Solving 'Inaccessible Folder' Issue: Fix Steps for Windows-Based PCs
- Solving Laptop Trackpad Issues on Windows 10, 8 & 7: A Comprehensive Guide
- The Complete Guide to OnePlus Nord CE 3 Lite 5G FRP Bypass Everything You Need to Know
- The Perplexity of Non-Existent Drive Letters in Windows Systems
- Top 5 Strategies to Eradicate Failed RPC in Windows
- Transforming How You Use the Mouse: Cross-Border Efficiency via PowerToys
- Title: Scaling Back Resource Usage by TiWorker.exe on Windows
- Author: Richard
- Created at : 2024-10-09 16:45:11
- Updated at : 2024-10-15 11:46:30
- Link: https://win11-tips.techidaily.com/scaling-back-resource-usage-by-tiworkerexe-on-windows/
- License: This work is licensed under CC BY-NC-SA 4.0.