Scouring System Files After Win-Blue Codes

Scouring System Files After Win-Blue Codes
When your computer crashes and you face a Blue Screen of Death (BSOD), your system saves the details of the crash as a BSOD log, in a pre-defined location in Windows. This information gives you details about when the crash happened, what caused it, and sometimes even what to do to fix the problem.
In this guide, we will first discuss where are the BSOD files located in Windows and then how to identify them. Once you have located a BSOD file, we will show you how to read it properly to understand the potential causes of the error and resolve the problem.
Disclaimer: This post includes affiliate links
If you click on a link and make a purchase, I may receive a commission at no extra cost to you.
Where Are the BSOD Log Files Located in Windows?
You can find the BSOD log files in the Event Viewer, Control Panel, and Registry Editor in Windows. Below, we have listed the detailed steps for finding these files in all three of these utilities.
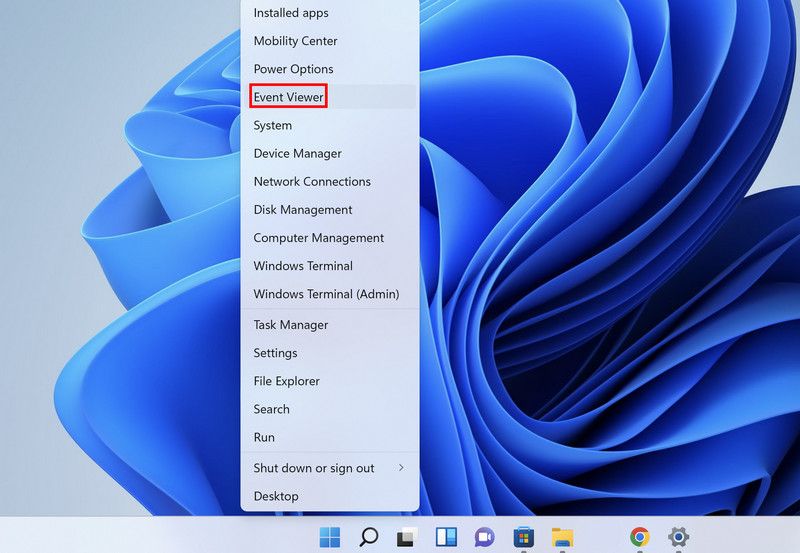
1. Find and Read the BSOD Log Files in the Event Viewer
The Event Viewer is a tool developed by Microsoft for users to view system and program-related events in Windows. These events can include system errors, warnings, informational messages, and more. In other words, every issue you encounter (whether a minor glitch or a major crash) will be logged in the Event Viewer for later investigation and sharing with Microsoft.
You can check out our detailed guide on what the Event Viewer is and how it can be useful if you are unfamiliar with it.
Here is how you can find the BSOD log files in the Event Viewer:
- Right-click on the Windows icon in the taskbar and choose Event Viewer from the context menu.

- Head over to the Action menu located at the top, and choose Create Custom View from the context menu.
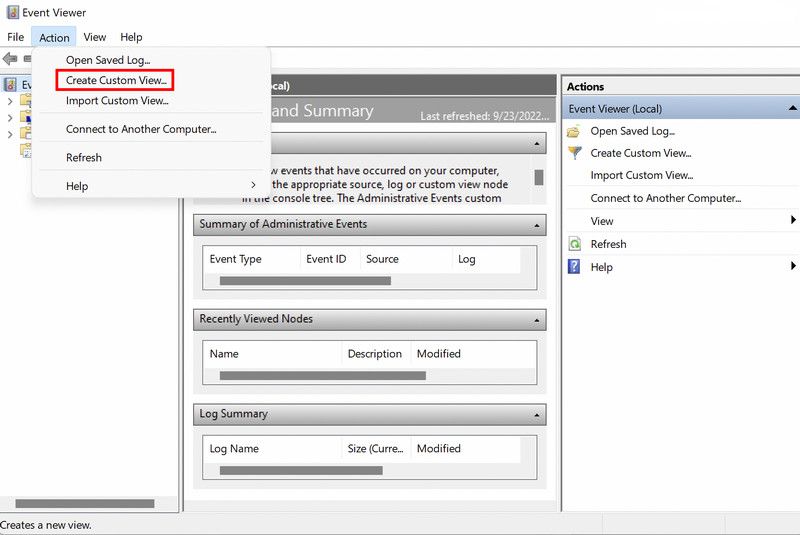
3. In the following dialog, expand the dropdown for Logged and choose the time when you encountered the issue.
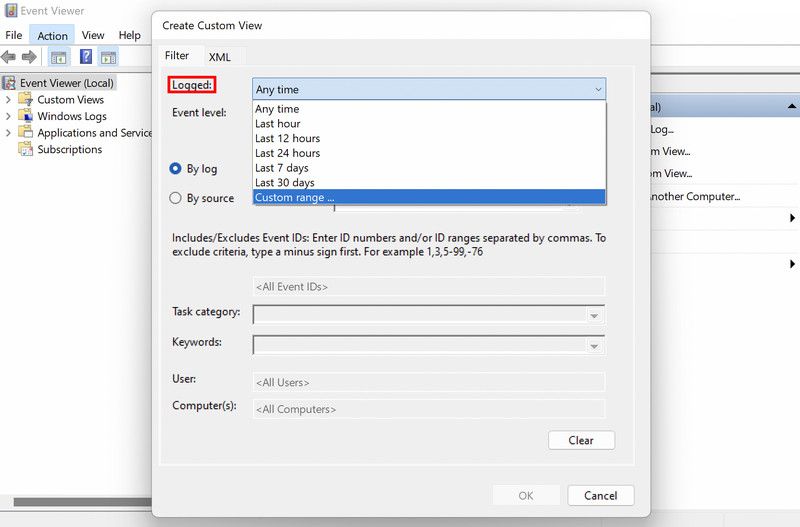
4. Now, move to the Event Level section and choose Error.
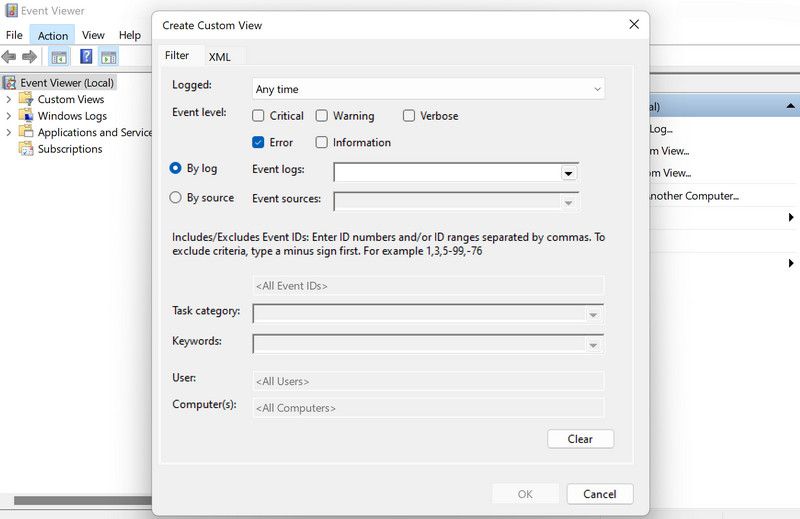
5. Expand the dropdown for Event Logs and checkmark the box for Windows Logs.
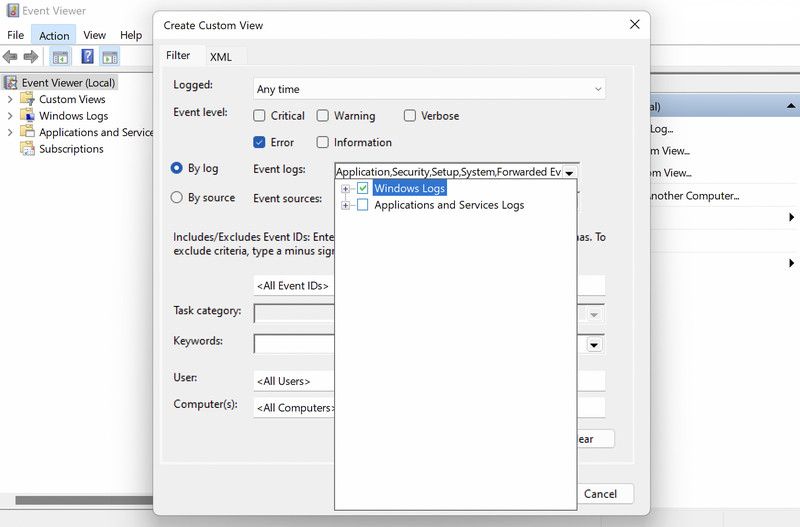
- Click OK to proceed.
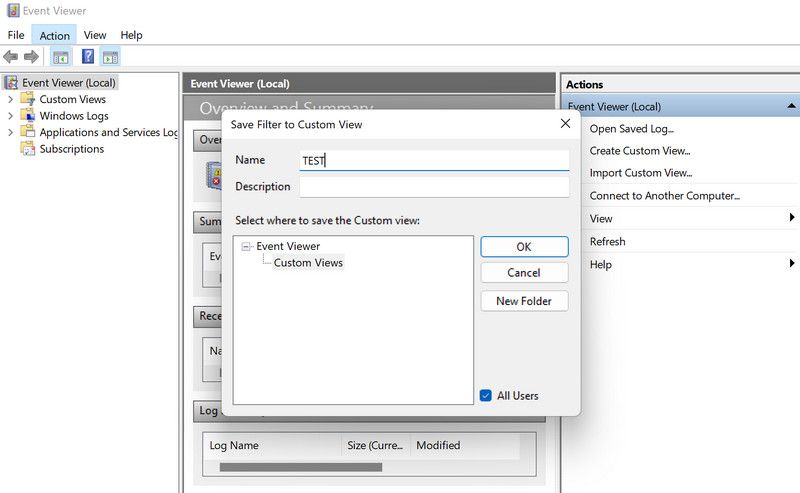
- You will now be prompted to enter a name and description for the custom view you just created. Enter these details and click OK.

- Once the view is created, you will be presented with a list of errors that occurred during the time frame you selected earlier. You can sort this information further in the Date and time section.
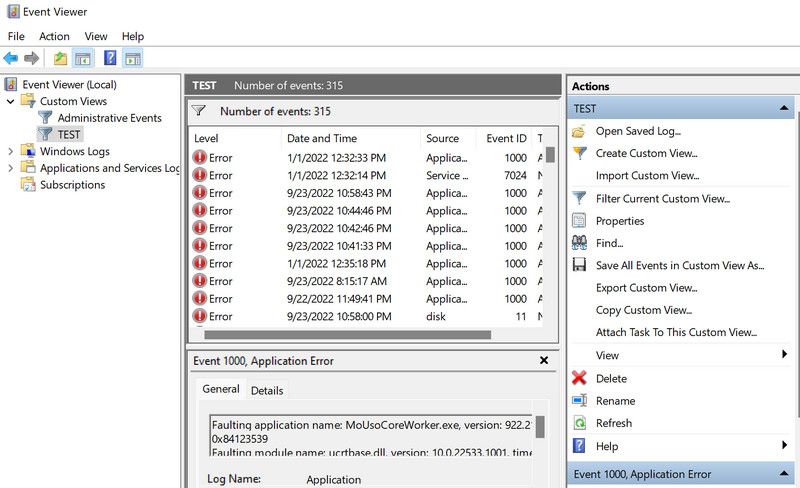
4. Next, locate the BSOD using details like the date and time again.
- Once you find the targeted log, click on it.
- Check both the General and Details tabs to get information about this error.
Once you find the error code associated with the crash and the cause, you can look for solutions online, or head over to our guide that discusses how to fix blue screen errors in Windows if it’s a bsod.
2. Find and Read the BSOD Log Files in the Registry Editor
In case using the Event Viewer does not work for you for some reason, you can use another Windows utility to locate and study the BSOD log files—the Registry Editor.
Windows Registry Editor is an administrative-level utility that lets you control how Windows operates and interacts with hardware and software. The Registry stores information related to the hardware and software components of your system. This information in the Registry is stored in the form of keys and values, and by modifying these with the dedicated Registry Editor, you can customize the operations of your system.
Listed below are the steps for finding the BSOD log files in the Registry Editor. Make sure you are logged into your system as an administrator before you proceed.
Press the Win + R keys to open Run.
Type “regedit” in Run and press Ctrl + Shift + Enter to launch the Registry Editor as an administrator.
Now, select Yes in the User Account Prompt.
Once you are inside the Registry Editor, navigate to the following location:
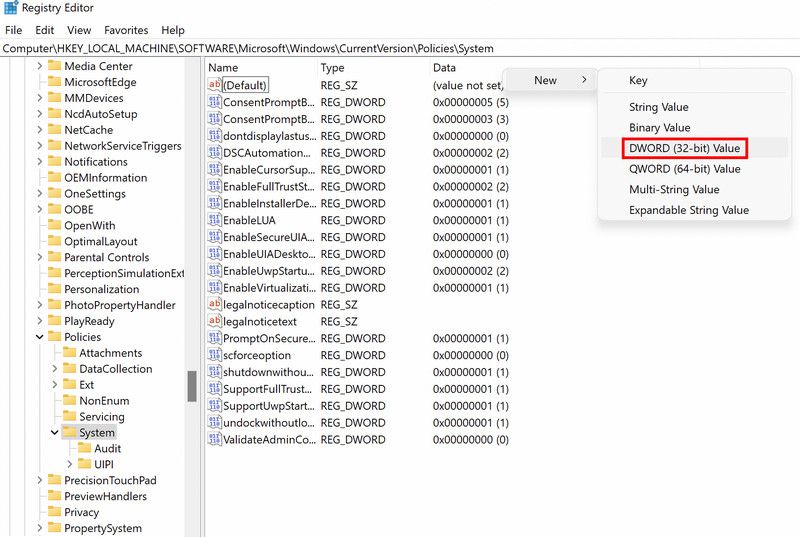
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\System\CurrentControlSet\Control\CrashControlNext, move to the right pane and right-click on an empty space anywhere.
Choose New > DWORD (32-bit) Value.

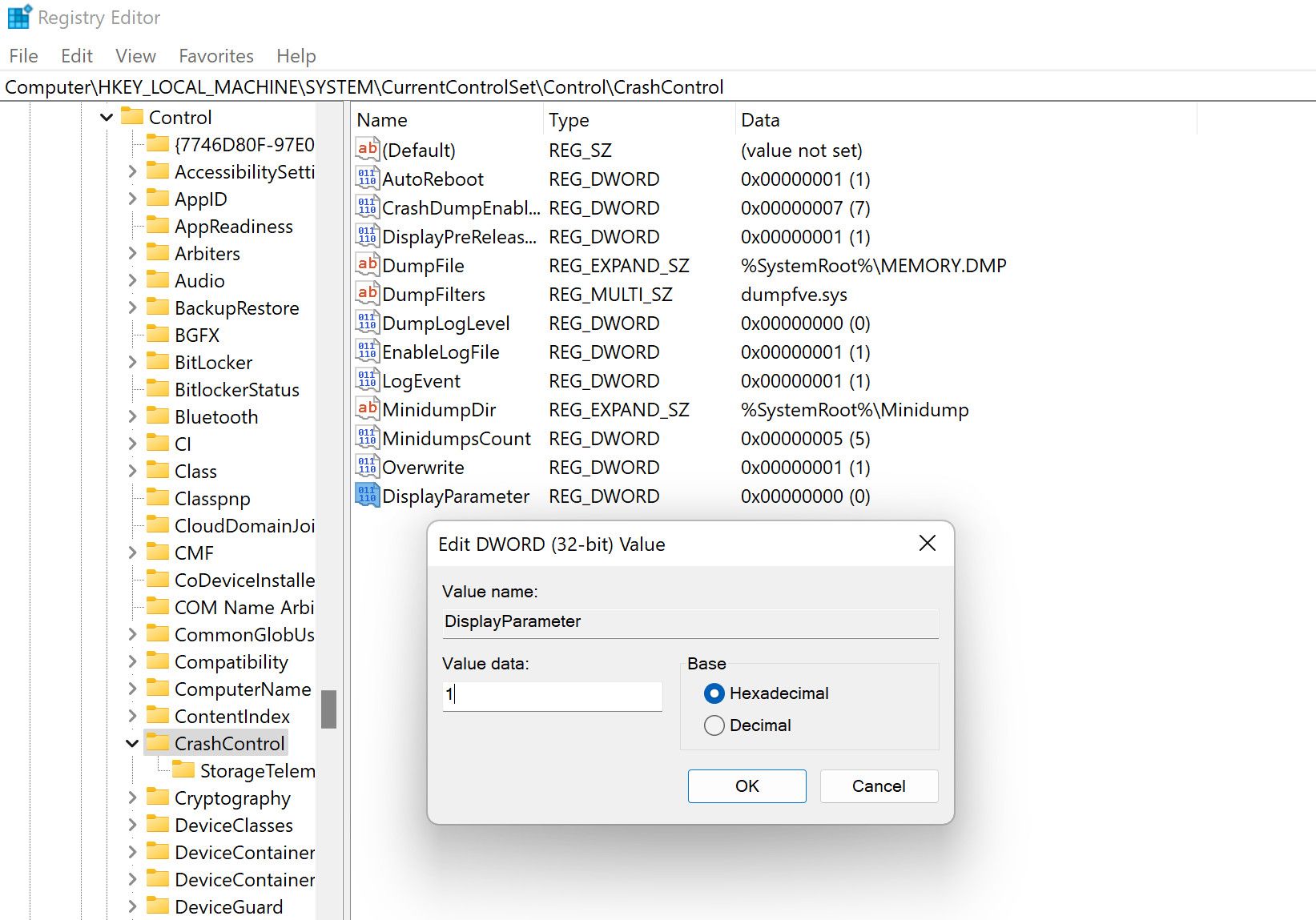
Name this value as DisplayParameters and double-click on it.
Under Value data, type 1 and click OK.

Once done, restart your PC.
Upon reboot, you should be able to view the log files without any problems.
3. Find and Read the BSOD Log Files in the Control Panel
The third way of finding and reading the BSOD log files is via the Control Panel. This approach offers a graphical representation of the log files using the Windows Reliability Monitor, unlike the methods we have explored previously.
The Reliability Monitor, which is different than the Performance Monitor (see Reliability Monitor vs. Performance Monitor ) will show you a timeline of important system events that occurred on your computer including BSOD occurrences, software installations, application crashes, and other relevant events.
Here is how you can use it to identify and fix problems that may affect your system:
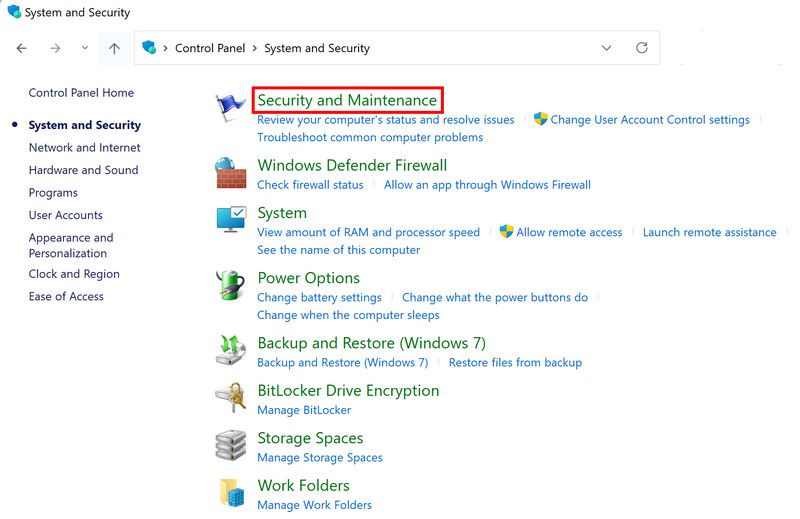
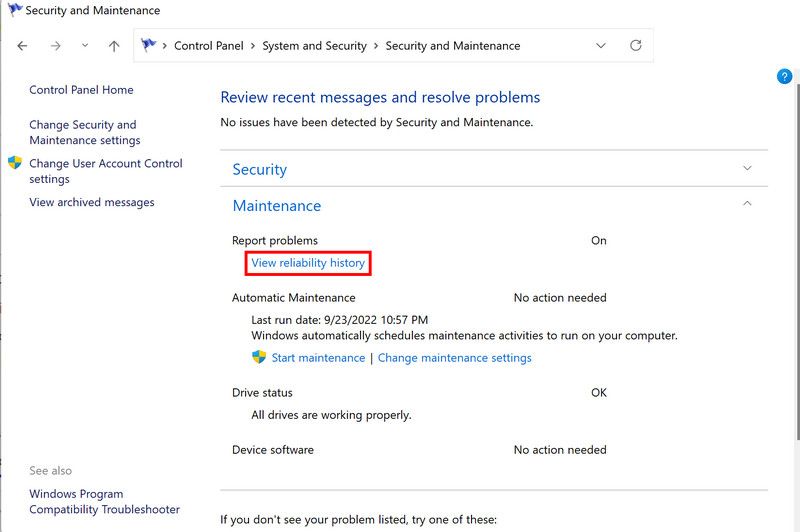
- Type Control Panel in the search area of the taskbar and click Open.
- In the following window, choose System and Security > Security and Maintenance.

- Click on Maintenance and then select View reliability history.
4. You should now see a graph showing the reliability data. Look for red cross icons and blue (i) icons in the graph, as they show problematic events.
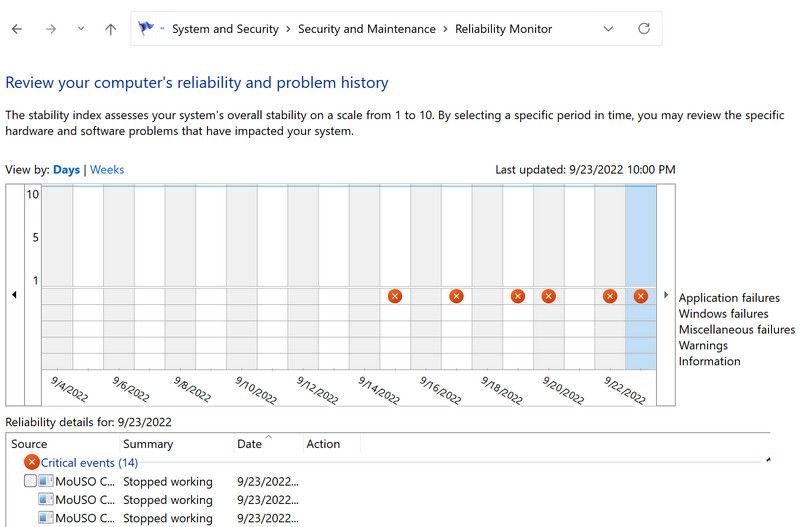
5. Click on each of the icons to view its details. Keep repeating the process to locate the event you are looking for.
You will be presented with information like the faulting application path, its name, fault module timestamp, exception code, etc. If this app caused a BSOD crash, then you can try ending its process via the Task Manager or uninstalling the app if it is not necessary.
It is also a good idea to copy this information and send it to Microsoft for review if you cannot find a solution online.
Learn How to Read Your BSOD Log Files and Resolve Your Crashes
Windows blue screen errors are nothing new, but since they only display messages like “Your PC encountered a problem” without describing the cause, it can be difficult to find a fix. Understanding how to read BSOD log files can not only help you identify the exact cause of the problem but also help you find the right solution.
Whenever a component causes your system to crash, you can disable it and switch to a better alternative to avoid the problem.
In this guide, we will first discuss where are the BSOD files located in Windows and then how to identify them. Once you have located a BSOD file, we will show you how to read it properly to understand the potential causes of the error and resolve the problem.
Also read:
- [New] Alternative Game Capture Software No More FBX Dependence for 2024
- [Updated] In 2024, Unlocking the Full Potential of Your Instagram Story with Multiple Images
- [Updated] Virtual Frontiers Five Incredible Upcoming PSVR Games
- Discovering Apple's Quietly Revolutionary AI Capability Poised to Shine at the Upcoming WWDC Insights
- Enable Dark Scheme in Windows Calculation App
- How to Fix the “We’ll Need Your Current Windows Password” Error on Windows 11 & 11
- In 2024, A Detailed VPNa Fake GPS Location Free Review On Poco C51 | Dr.fone
- In 2024, Views That Pay the Bills The Youtube Metric
- Irreversible Integration of TikTok Profile Linking Technique
- Rebels Of Kindness | Free Book
- Secret Passages to Your PC: Mastering RDP on Win 11
- Strategies to Shave Time Off Epic Launcher Downloads
- Windows 11' Writers’ Choice for Best Video Edits
- Title: Scouring System Files After Win-Blue Codes
- Author: Richard
- Created at : 2025-03-02 23:59:04
- Updated at : 2025-03-04 20:38:17
- Link: https://win11-tips.techidaily.com/scouring-system-files-after-win-blue-codes/
- License: This work is licensed under CC BY-NC-SA 4.0.