
The Right Way to Hibernate Windows Computers

The Right Way to Hibernate Windows Computers
Windows offers three power options: sleep, hibernate, and shutdown. Microsoft also added an option called Fast Startup which enables the PC to boot faster.
But have you wondered which power option is the best for you? Which one saves more power or which one loads the desktop faster? Let’s explore each one.
Disclaimer: This post includes affiliate links
If you click on a link and make a purchase, I may receive a commission at no extra cost to you.
What Does Each Windows Power Option Do?
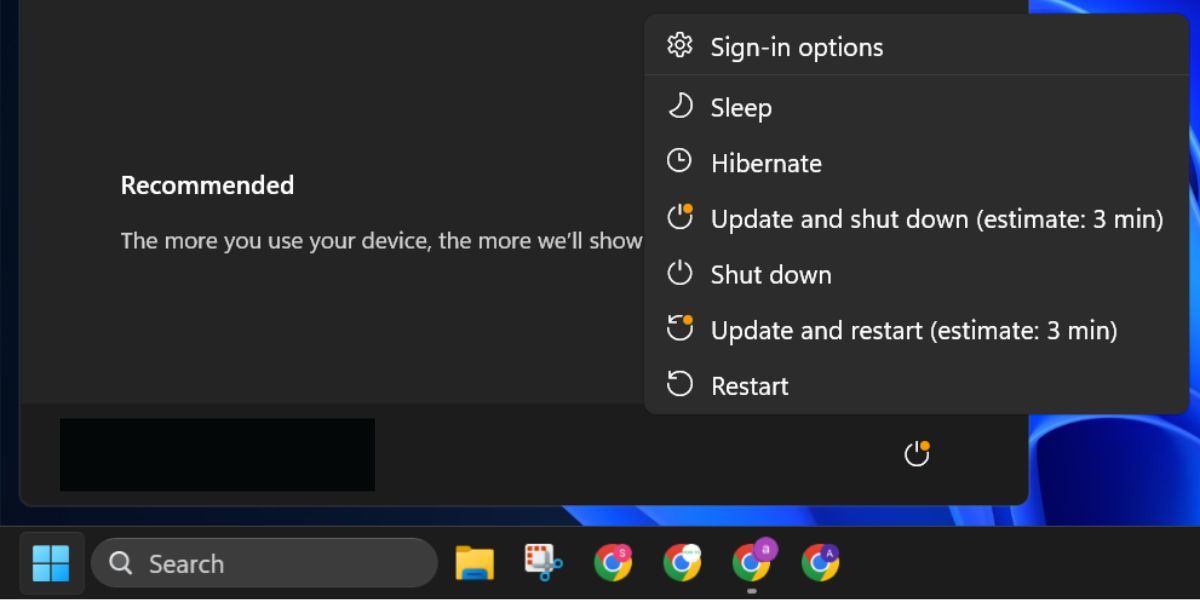
Before we jump into which option is best for you, we have to break down what each one does.
What Does Hibernation Do on Windows?
Hibernation mode saves all the contents of the RAM in a file on your hard disk or SSD. This includes all your running processes, open applications, and any data entered into them.
Once your processes are saved onto the storage drive, hibernation powers off your PC. You can power on your PC whenever you need, and it will load up all your apps and processes back up instantly.
Hibernation mode is designed to preserve the current state of Windows, even if the power is cut off. Once you hibernate your PC, you can disconnect it from a power source and keep everything intact for when you plug it back in.
However, it takes some time to hibernate the PC because it writes the RAM contents to the hard disk, especially when you have lots of apps open.
What Does Putting Your PC to Sleep Do on Windows?
Sleep mode puts your PC in a low power mode, but continues to supply power to the RAM. This means that your PC will remember all your open apps and system processes. You can then wake your PC from sleep and not lose any data in the process.
Sleep mode is designed to save on power while keeping the RAM “awake.” This means when you put the PC to sleep and wake it up again, it can suspend and reload all your apps a lot faster than either hibernation or a full shutdown.
The caveat is, that if your PC loses power or your laptop runs out of battery charge, the power to the RAM will die and cause Windows to forget everything that was open. As such, you’ll need to keep your machine constantly supplied with power while it’s sleeping.
What Does Shutting Windows Down Do?
Shut down closes all the open apps and system processes and then power off your PC. Nothing is preserved, and you will have to restart the PC, complete the entire boot process, and then boot to the lock screen. It is the slowest of all the three methods.
Shutting Windows down completely cuts the power to your PC after closing all the applications and background processes. It doesn’t retain anything, and you will have to boot the PC again and reopen all the applications. Your PC will take a considerable amount of time to load Windows as compared to Hibernate and Sleep mode.
Should You Use Hibernate, Sleep, or Shut Down?

Hibernate is well-suited if you want to save the system state for an extended period of time. It is also helpful if the battery levels are low, and you don’t have access to a power source. In this case, you can hibernate the PC and not worry about losing any progress while saving power.
Sleep mode is useful when you have access to a power source and will be away from your PC for a small amount of time. So, if you want to take a quick break, and your PC has adequate battery levels or an uninterrupted power supply, you can put the PC in sleep mode.
Lastly, shut down your PC if you don’t need to keep any of the apps or programs remain open. Windows 10 and 11 also come with Fast Startup which hibernates kernel-level processes to help boot the PC faster. But you can disable Fast Startup if you prefer to completely shut down your PC and start afresh every time.
Whichever method you pick, you can check out how to shut down or sleep Windows with a keyboard shortcut for faster results.
Pick the Appropriate Power Option When Using Windows
Both Sleep Mode and Hibernate help you preserve your PC state and not lose any progress. So, you can use any of these two features to save time and reduce power consumption. After you are done with your daily tasks and don’t need the PC anymore, shut it down.
But have you wondered which power option is the best for you? Which one saves more power or which one loads the desktop faster? Let’s explore each one.
Also read:
- [New] Directly Embedding Google Meet in YouTube's Video Library
- [New] In 2024, The Blue Badge Breakdown A Guide to Social Media Credibility
- [Updated] In 2024, Breakdown of Profit From a Million Youtube Watches
- 2024 Approved Mastering Narratives The Science and Art of Crafting Memorable FB Stories
- Addressing Missing D3DX9_39 DLL in Win11
- Charkas Para Todos | Free Book
- Edit and Send Fake Location on Telegram For your Samsung Galaxy F54 5G in 3 Ways | Dr.fone
- Enhancing Your Written Workflow with LibreOffice Vs. Google Docs: Key Advantages for the Serious Writer
- File System Exploration in Win11: 6 Keyways to Duplicating File and Folder Paths
- Fixing Low Memory Warning in VmWare-Hosted Windows Environments
- How to solve MKV lagging problem in HTC U23 Pro?
- Master Your Windows Startup: The Comprehensive Guidebook
- Mastering Windows Automation for Batch Files
- Minimizing Browser Heft: Comparing Best Options for Low RAM Usage
- Simplify Digital Management with Windows' Automatic File Disposal
- Steering with Apple Maps From a PC
- Tackling Frozen Volume Shadows in Operating Systems
- Title: The Right Way to Hibernate Windows Computers
- Author: Richard
- Created at : 2024-11-30 01:57:58
- Updated at : 2024-12-06 17:58:29
- Link: https://win11-tips.techidaily.com/the-right-way-to-hibernate-windows-computers/
- License: This work is licensed under CC BY-NC-SA 4.0.