Tips for Troubleshooting Windows Registry Issues

Tips for Troubleshooting Windows Registry Issues
The Windows Registry is a crucial system component best left unaltered. But the registry grows bigger and older with time and can have a lot of broken or corrupt items. Oftentimes, some registry entries remain even after you uninstall a program on your system.
Broken registry items can lead to system errors and hamper your system’s normal functioning. But don’t worry! We will explain the importance of the Windows Registry and list out multiple methods to fix the issue and avoid them in the future.
Disclaimer: This post includes affiliate links
If you click on a link and make a purchase, I may receive a commission at no extra cost to you.
What Is the Windows Registry?
The Windows Registry stores the necessary configuration settings which a Windows system component or a program needs to run properly. Tweaking enthusiasts can tinker with registry entries and even create new ones to modify the behavior of a program. You canactivate hidden Windows 11 themes by altering the registry values.
It may sound exciting to tweak the Windows Registry and unlock new features. However, you must never change, add, or delete any entries in it unless instructed to do so by a trusted source. If you’re not careful with how you edit the Registry, you can do serious harm to your PC.
However, the Windows Registry isn’t impervious to errors. These errors can arise due to malware infestations, unexpected power failures, and corrupt or outdated entries.
How to Fix Broken Registry Items in Windows 11
Try out the following methods to fix the broken registry items on your Windows 11 system:
1. Use the Disk Cleanup Tool
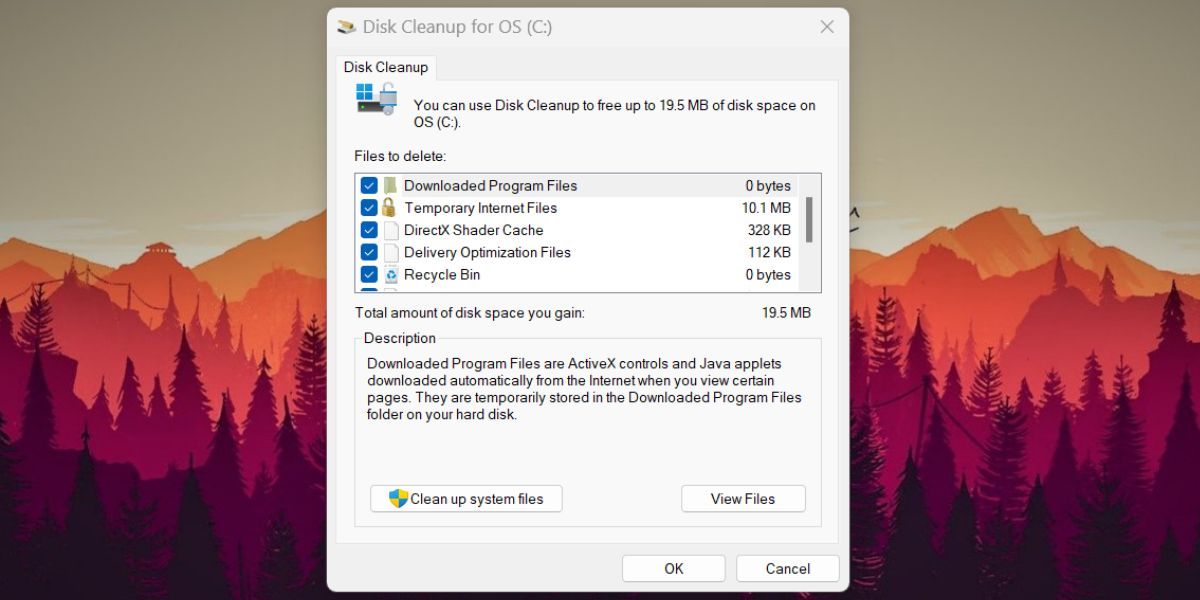
Rather than installing a third-party cleanup tool, try the Windows Disk Cleanup utility. It is an old yet trustworthy utility included with every copy of Windows OS. You can use it to clear system clutter which also clears registry associations of some apps. Repeat the following steps:
- PressWin + R tolaunch the Run command box . Typecleanmgr in the text input box and press the enter key.
- Disk Cleanup tool will launch. Select theC drive and click on theOK button.
- Navigate down and click on theClean up system files button.

- The Disk Cleanup tool will launch again. Keep the Drive selection asOS (C:) and click on theOK button.
- Wait for the utility to scan the system. Then, click on theOK button.
- Disk Cleanup will reconfirm your decision. Click on theDelete files button.
2. Try the Automatic Repair Tool
Microsoft offers an automatic repair tool that can fix system boot issues and even core system registry files. Here’s how to use the tool:
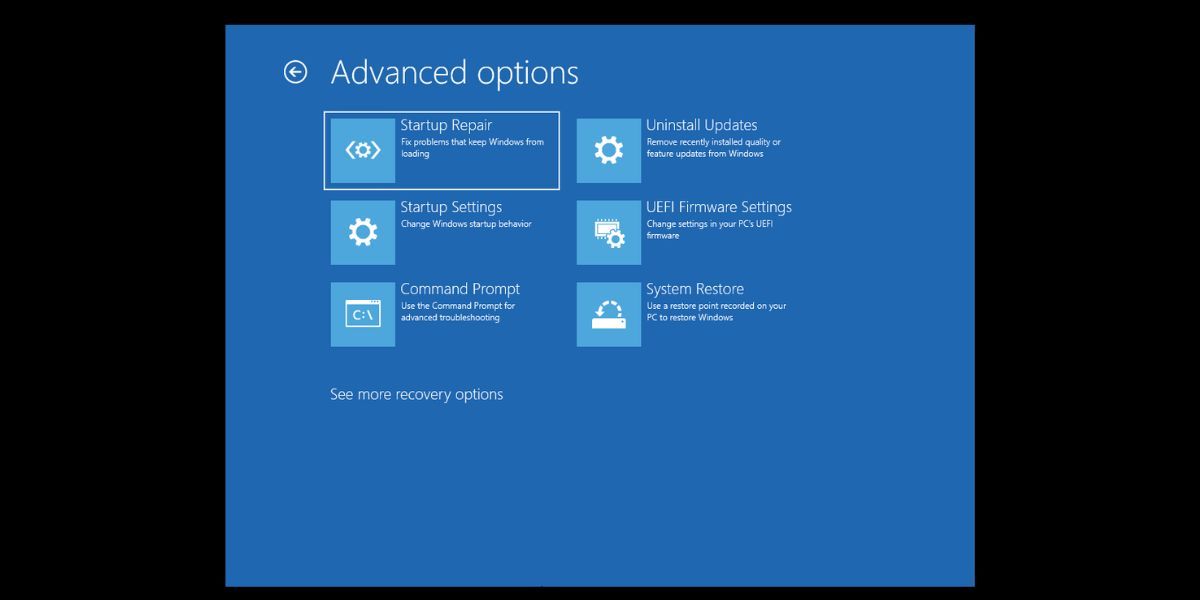
- PressWin + L to sign out of Windows. Click on thepower icon in the bottom-right corner.
- Then, press and hold theShift key and click on theRestart option.
- Windows will restart and boot to the Windows Recovery options page. Navigate toTroubleshoot > Advanced options .
- On theAdvanced options page, select theStartup Repair option.

- The utility will begin diagnosing your system and attempt repairs. After that,restart your system.
3. Run an SFC Scan
SFC is an inbuilt windows utility that can scan your system for corrupt or missing system files. It will then replace all the corrupt or missing files with a fresh copy. Here’s how you can scan your system with SFC:
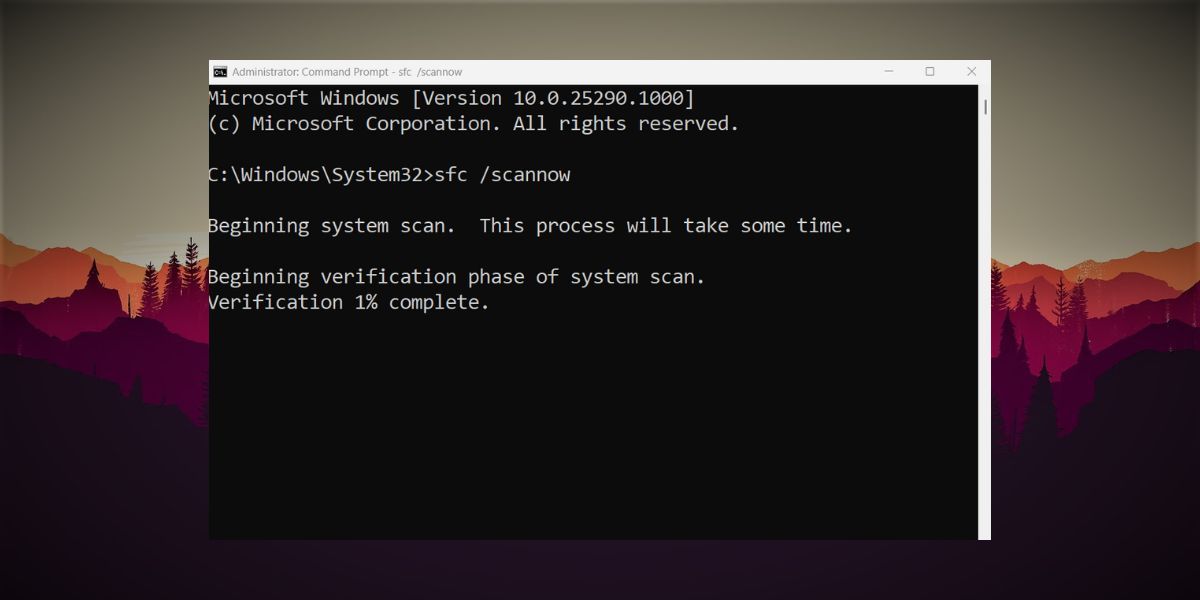
PressWin + R to launch the Run command box. In the text input box, typecmd and then pressCtrl + Shift + Enter at once.
A command prompt window will launch with administrator privileges.
Now, typesfc /scannow and pressenter to execute the command.

Patiently wait for the utility to scan and replace files on your system.
Close the command prompt window and restart your computer.
4. Try a DISM Scan
DISM is also a command line tool, but it can scan and repair Windows System Image files. The utility can work in both online and offline modes. Repeat the following steps to run a DISM scan:
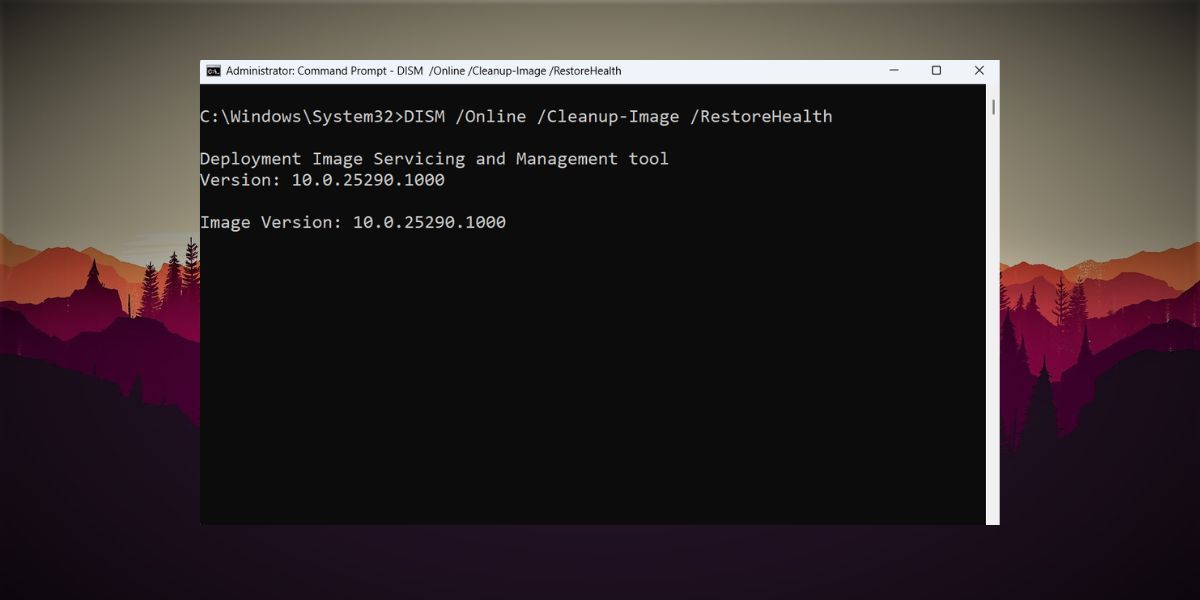
- PressWin + S to launch Windows search. Search forCMD , and select theRun as administrator option from the right pane.
- Once CMD launches with elevated permissions, typeDISM /Online /Cleanup-Image /RestoreHealth command and press theenter key.

- Wait for the tools to scan and repair the problems with the system image.
- Finally,close the command prompt and restart your PC.
5. Import an Old Registry Backup
If you have a habit ofcreating registry backups on Windows , it could solve the broken registry items issue with your system. When you encounter issues, you can import the old registry backup when the system was working fine.
Here’s how you can import an old backup in Windows Registry:
- PressWin + R to open the Run dialog box. Then, enterregedit in the text box and press theEnter key to launch the registry editor.
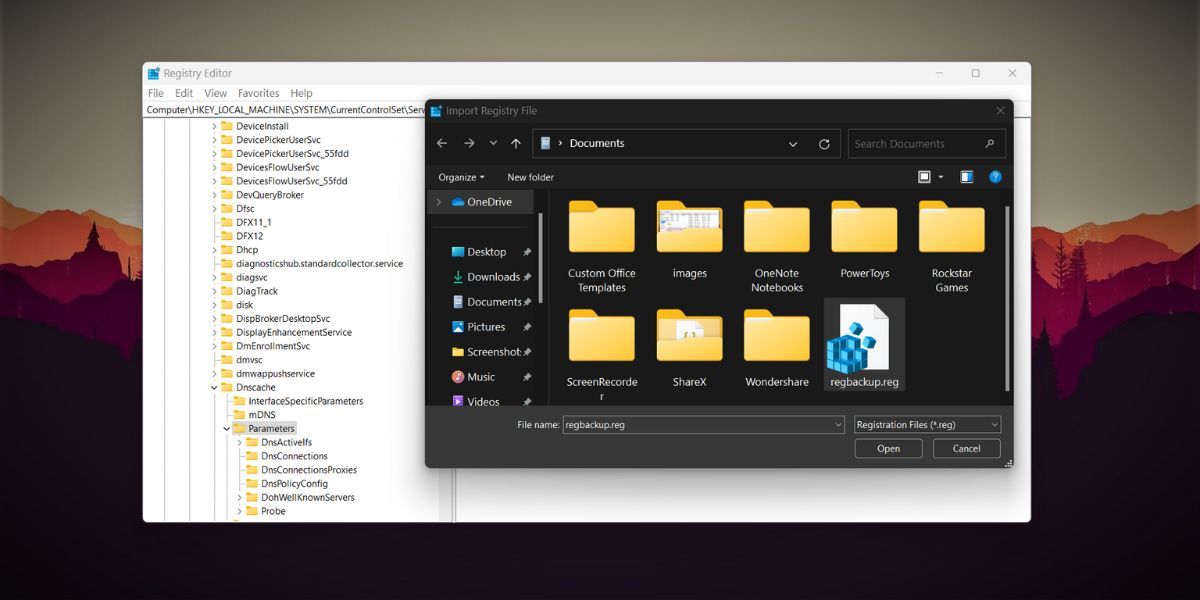
- Go to the top bar in the Registry Editor window and click onFile > Import .

- Navigate to the registry backup file location on your system.Select the registry file and click on theOpen button to begin importing the file.
- Wait for a few minutes for the import to complete.Restart your system.
6. Check for Malware on Your System
Malware can create and modify the registry items, and can even break or corrupt existing registry entries. You must perform a thorough scan of your Windows computer using Windows defender.
Here’s how to do a complete system scan using Windows Defender:
- Open the Start menu and searchWindows Security .
- Click on the relevant search result to launch the app.
- Navigate toVirus and threat protection > Scan options .
- Select theFull Scan radio button and then click on theScan Now button.
- Windows Security will execute a deep scan of all the files on your disk. If it finds any traces of malware, manually remove them from your system.
7. Do a System Restore
The System Restore tool saves all Windows system files and drivers including the registry contents. If none of the above methods work, you can revert to a last known good system configuration using a restore point.
Repeat the following steps to perform a system restore:
- PressWin + R to launch the Run command box. Typerstrui into the text box and press theEnter key.
- System Restore utility will launch on your system. Click on theNext button to continue.
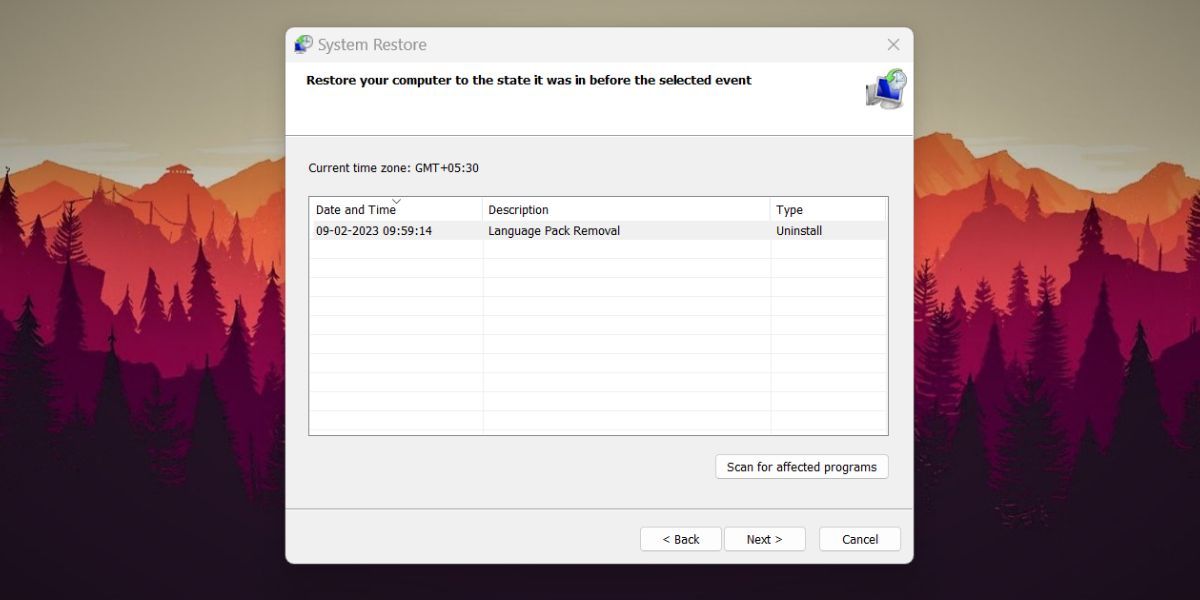
- You will see a list of all the available restore points created by program installations or Windows updates.
- Select the most recent restore point from the list and then click on theScan for affected programs button. Note down these programs or take a screenshot because you will have to reinstall them again.

- Click on theClose button. In the System Restore window click on theNext button.
- Confirm your restore point selection and click on theFinish button.
- Your system will restart automatically to apply the restore point. It will then automatically boot to the desktop.
8. Reset Your PC
If System Restore fails to do the trick, you are left with the last arrow in your troubleshooting quiver:performing a factory reset on Windows . It will wipe all the drivers and programs and revert the system to a clean state. However, you can save your files and documents if you pick theKeep my files option while resetting your Windows 11 computer.
Keep Your Registry Safe From Corruption
If your Windows Registry has seen better days, start by running disk cleanup and SFC and DISM scans. Then scan your system for malware infestation and import an old registry backup (if you have one). Lastly, leverage the system restore utility or reset your Windows PC.
Also read:
- [New] Transforming YouTube Content Using the Power of iMovie for 2024
- [Updated] A Deep Dive Into Toolwiz App for Professional Photos
- [Updated] Budget-Friendly Airborision Top 5 Under $500 Drone Picks
- 2024 Approved Unveiling Video Visionaries Subscriber Top 5
- 21 Pioneering Metaverse Ventures for Insightful Discussion for 2024
- Cracking Down on Distorted Sounds: Fix Your Windows 10/7 Speaker Problems
- Decision Guide: Choosing a Superior Windows Coder
- Detailed guide of ispoofer for pogo installation On Oppo A1 5G | Dr.fone
- Efficiently Detect PC's Network Settings in Windows PS
- Elevate Security with Extended PINs on Win10/11
- Erfolgreiches Replacement Für SuperDuper: Die Top-Wahl Für Nutzer Von Windows 11 Und 7
- In 2024, A Step-by-Step Guide on Using ADB and Fastboot to Remove FRP Lock on your Itel P55
- Minimizing High CPU Drain From Dropbox: A Guide for Windows Users
- Rejuvenate Right-Click Menus with Effective Fixes
- Simplify Multidevice Scribbling with WIN11'S Notes Feature
- Tailor-Made Interface: Task Manager on Win11
- The Ultimate Guide to 20 Critical Command Prompt Commands
- Title: Tips for Troubleshooting Windows Registry Issues
- Author: Richard
- Created at : 2025-02-12 01:41:33
- Updated at : 2025-02-16 03:46:06
- Link: https://win11-tips.techidaily.com/tips-for-troubleshooting-windows-registry-issues/
- License: This work is licensed under CC BY-NC-SA 4.0.